

What do they express? To understand it better we are going to divide them into 3 categories Single Concept Modal: they have one meaning Double Concept Modal: they have two meanings Modals in past: They are used to express a situation in the past They can have more than one meaning depending on the situationsħ Categories Will Might Should Ought to Had better May Must Would Shall
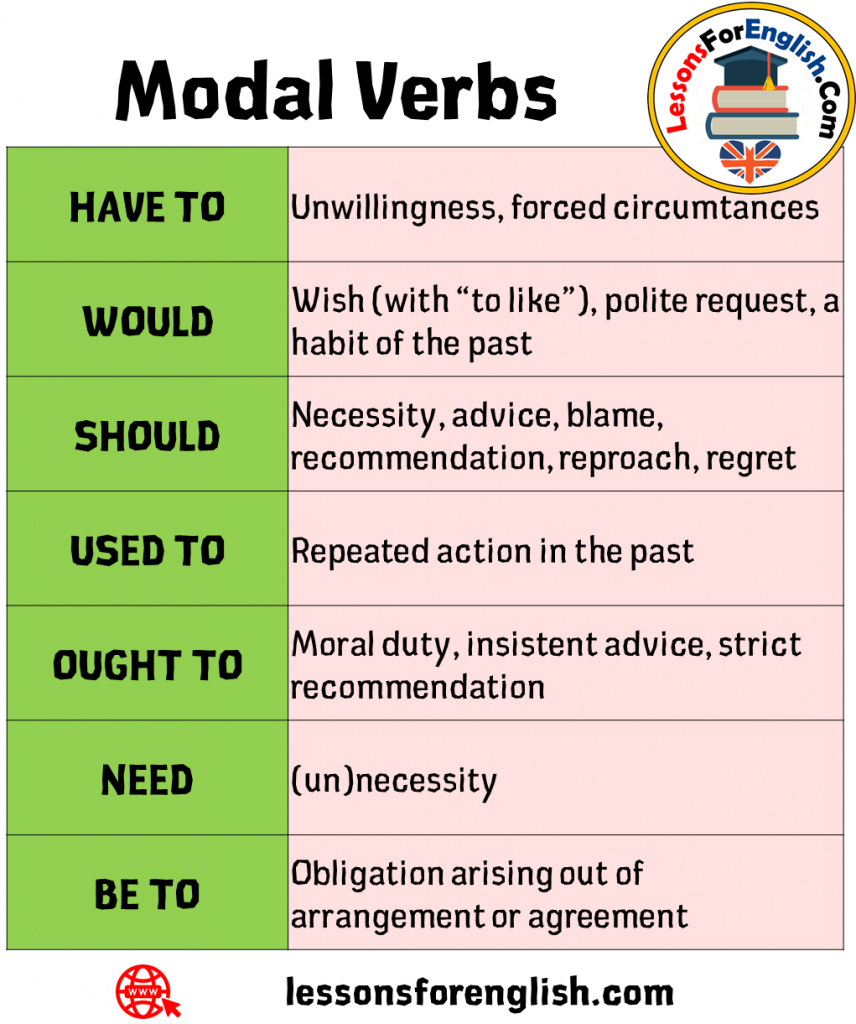
Modal verbs use other verbs to complete the tenses Can is completed with be able to Must is completed with have to You must come early They can play the piano They will be able to play the piano in the future You had to come early yesterdayĦ They can have more than one meaning depending on the situations To can / caning to must /musting She must study We should have gone the other way He could play football in his youth (general ability) Modal verbs do not have infinitives or –ing forms Modal verbs are followed by an infinitive without toĥ Form Modal verbs do not have all the tenses Would you like to come with me? Do you would like to come with me? They can’t be serious They don’t can be serious There is no “s” in singular There is no “do / does” in the question There is no “don’t / doesn’t” in the negativeĤ Form Modal verbs do not have infinitives or –ing forms How do we use modals? Example: Mary could play the piano S Subject V Verb M They do not accept conjugation They do not need other auxiliary verbsģ Form He can ski He cans ski or He can skis Might Must Shall Should Will Would Ought to They are Auxiliary verbs that provide additional and specific meaning to the main verb of the sentence Modal verbs are sometimes referred to as Modal Auxiliary verbs because they help other verbsĢ They do not accept conjugation They do not need other auxiliary verbs 1 What are modal verbs? They are: Ought to Can Could May


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
